Have you ever wondered what lurks deep down in the ocean’s floor or in other bodies of water? Have you also thought about what creatures can be found even closer to the surface of the water, but are too microscopic to see? If so, then welcome to the fascinating world of plankton, where there is so much to learn.
As a type of plankton, zooplankton are oceanic drifters that play a vital role in the nautical ecosystem, especially the food chain of the ocean. Because they are too weak to swim against the water’s tides and currents, zooplankton must be carried by the waves, which is why they are known as drifters.
As you learn more about these organisms, there are many questions to be answered, such as “What do zooplankton eat?” and “Why are zooplankton important?”
So, without further ado, let’s dive right in and begin learning about these complex and interesting creatures of the water that make up the plankton population.
What Are Zooplankton?
The word plankton comes from the Greek word “planktos,” which means “drifter” or “wanderer.” Plankton are organisms that are carried by currents and tides because they are too weak to swim against the current. Instead, they are known for drifting along in the water.
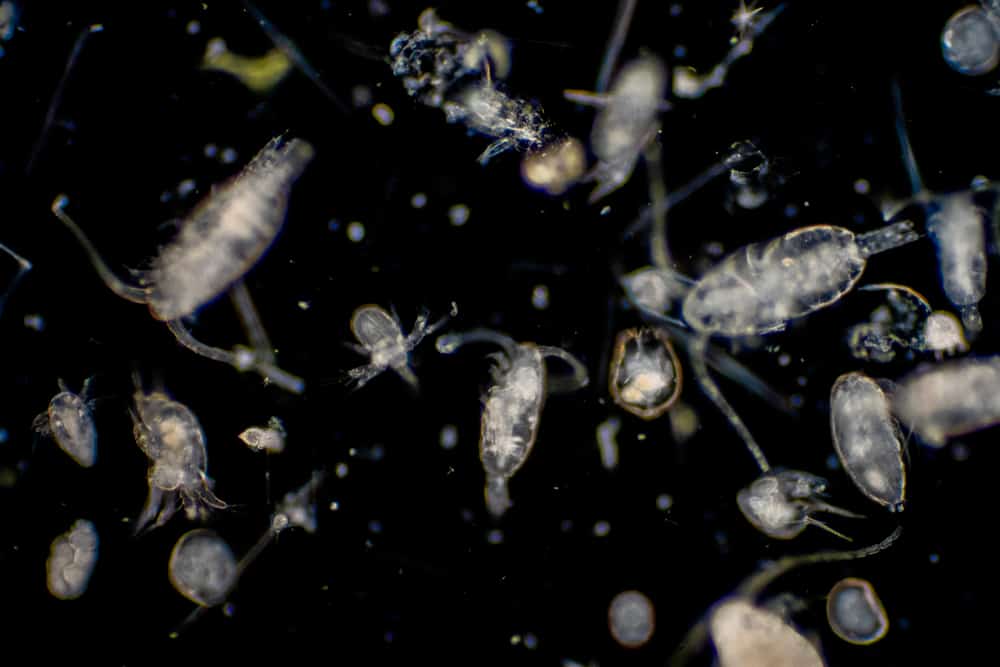
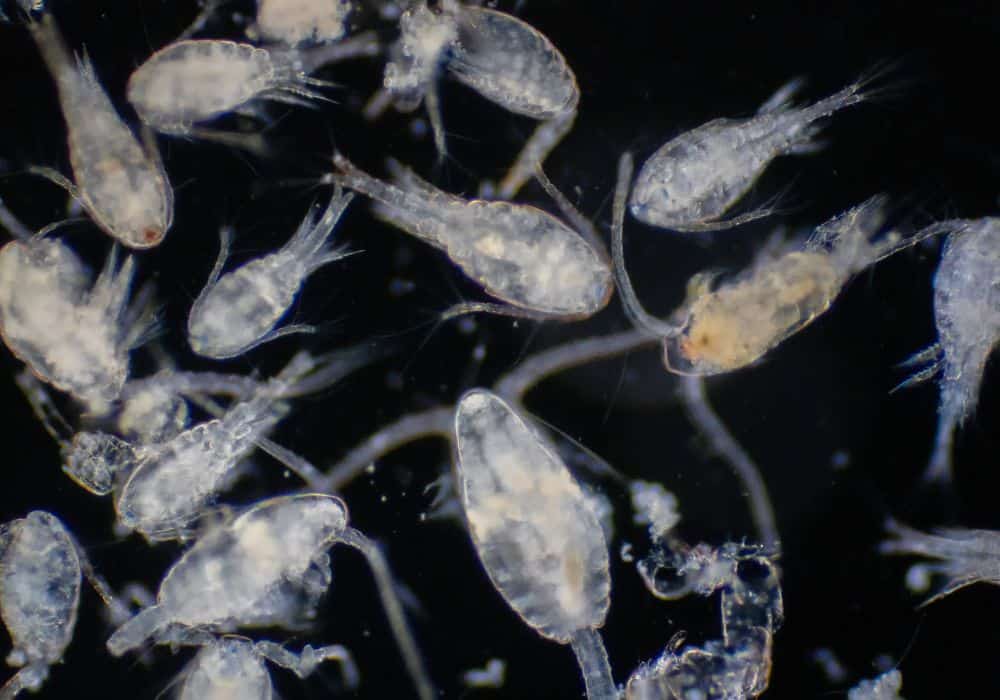
Plankton are classified by their size, type, and how much time they spend drifting in the ocean. These microscopic organisms are further subdivided into two categories: zooplankton, which function as animals, and phytoplankton, which function as plants.
Zooplankton are larger than phytoplankton and can include drifting animals of microscopic size; however, they can also include creatures as large as jellyfish. This type of organism can be found in many different bodies of water, including the ocean, lakes, and ponds. Unfortunately, they cannot survive in rivers or streams.
These complex creatures vary in size, ranging from a few millimeters to a size so small that you would need a microscope to see them. Here’s a breakdown of a few different types of zooplankton that drift along in the ocean.
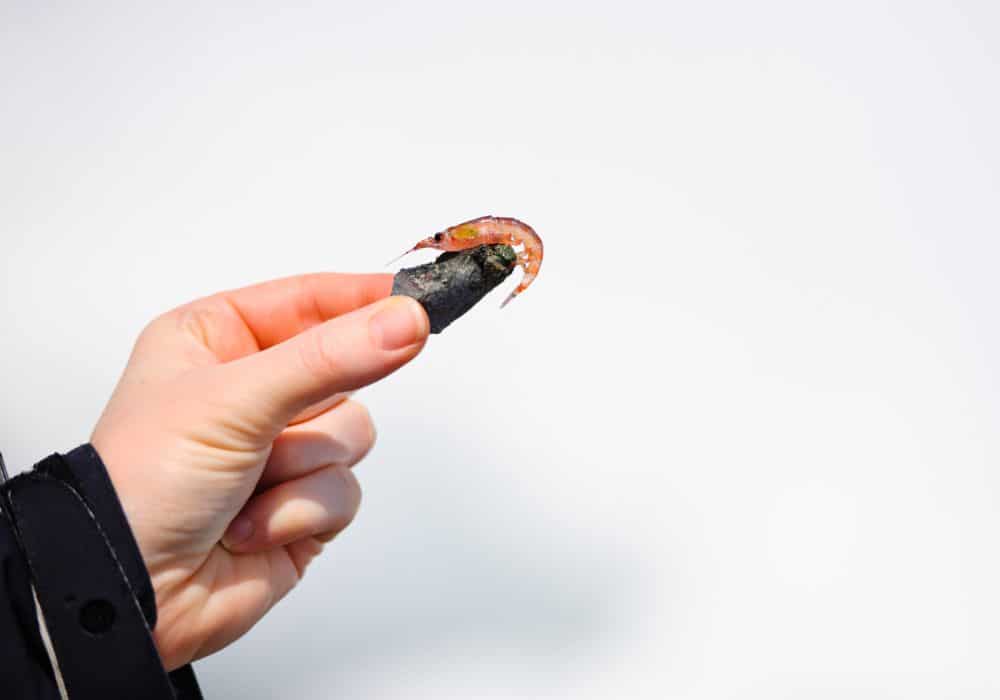
Krill
A type of crustacean, krill are found in oceans around the world. Like other zooplankton, they mainly feed off phytoplankton and other types of zooplankton. Krill measure about three centimeters, making them nearly microscopic in size.
While they are small, they play many important roles in the lives of other creatures in the ocean. Krill are known for playing a big part in the food chain of the ocean. They sit right at the bottom of the marine food chain, as many larger animals and organisms, including blue whales and seals, eat them as a primary food source.
There are plenty of krill to go around as these small organisms make up some of the ocean. During the night, krill can be found near the surface of the water, whereas they drift deeper into the water in the daytime.
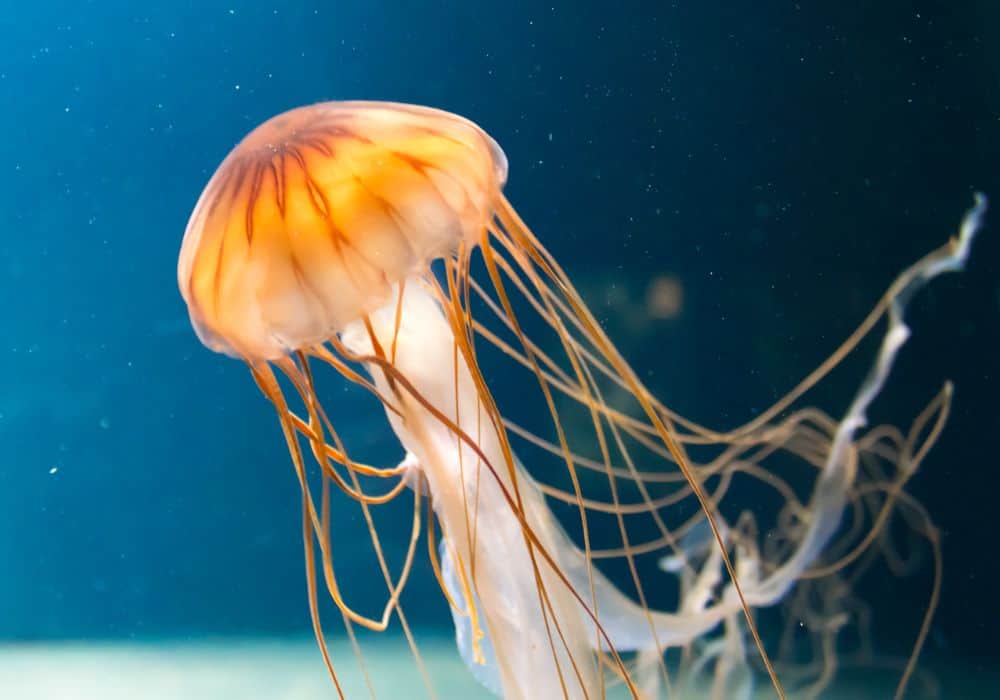
Jellyfish
As one of the larger zooplankton species, jellyfish are a type of cnidarian that can be found throughout the ocean. Some jellyfish reside near the surface of the water, while others are only found in deeper waters. Primarily, jellyfish are most common in coastal regions of the world.
Jellyfish are characterized as zooplankton because even though they are larger than most zooplankton, their ability to swim is still weak enough to be classified as such. Jellyfish belong to the same animal group as corals and sea anemones, and they swim by continuously pulsing their bells. They rely on the waves and current to help them move across long distances.
While they have nervous systems and organs, they have no hard body parts like other sea life. Instead, they have stinging cells that make up their tentacles. These stinging tentacles can be deadly to some water species. In addition, this is how they catch the plankton and larval fish that they eat.
Conger Eel
Like jellyfish, conger eels are also larger organisms. These zooplankton are found in the coastal regions in Europe and North America. For conger eels, their homes are farther from the surface of the water and closer to the ocean’s sediment. They feed on tons of crustaceans and small fish.
Segmented worm
Also known as leeches, segmented worms are commonly found in coral reefs and tidal zones. They reside deep inside of the sediment and are an important type of zooplankton for a few reasons.
By digging itself deep into the sediment, segmented worms are helpful in oxygenating the sediment, which accelerates the growth of other animals and oceanic species.
What Do Zooplankton Eat?
Zooplankton are mainly herbivores, which means that they usually feed on plants, not meat. In fact, most zooplankton eat phytoplankton, which are microscopic plants in the water that are too small for the naked eye to see. In this way, zooplankton begin the marine food web.
In addition to eating different types of phytoplankton, they also eat bacteria and algae that lie at the bottom of the food chain. In rare cases, zooplankton may also feed off each other at times.
What Animals Eat Zooplankton?
Most zooplankton feed on phytoplankton, or smaller plants. However, zooplankton are often eaten by larger animals, such as fish, small sharks, and baleen whales.
To camouflage into their environment and to avoid being eaten, some zooplankton are equipped with clear shells that allow them to hide from predators, such as fish, squid, crabs, rockfish, anchovies, and larger marine life species.
Where Do Zooplankton Live in the Ocean?
While zooplankton have made just about every inch of the ocean their home, the majority of this species can be found in the upper to lower ocean. This is because the upper part of the ocean is where their main food source, phytoplankton, resides.
As mentioned before, while some zooplankton may live in the ocean, other zooplankton may reside in other bodies of water, such as lakes and ponds. It is very rare, however, to find zooplankton in rivers and streams.
Why Are Zooplankton Important?
Ultimately, zooplankton are important because of the role they play in the aquatic food chain. Zooplankton are the key link between phytoplankton and larger ocean animals.
Zooplankton can also play a vital role in affecting the water quality of the areas they reside in. If there were less zooplankton around, ocean life would be on a sharp decline. This is because zooplankton are an important food source for many creatures of the ocean.
FAQs
Are you curious to learn more about zooplankton and who they really are? Check out our frequently asked questions (FAQs) for everything you need to know about this complex marine life species.
Is zooplankton a primary consumer or producer?
Although they may be small in size, zooplankton are primary consumers in the ocean. This is because they feed on smaller phytoplankton in the ocean, however, they are fed on by other consumers in the ocean, such as larger fish, which are higher up in the food chain.
Phytoplankton, on the other hand, would be an example of a primary consumer, because they create their own food. As previously mentioned, phytoplankton use photosynthesis to convert carbon dioxide and other valuable nutrients into carbohydrates and oxygen. As a result, these carbohydrates can then serve to nourish other marine life.
What’s the difference between zooplankton and phytoplankton?
The main difference between zooplankton and phytoplankton is that zooplankton are animals and protozoa, while phytoplankton can be classified as ocean plants, or photosynthetic organisms, such as algae and protists.
Like any plant, phytoplankton are responsible for conducting photosynthesis, in which they convert the sun’s rays into energy and produce oxygen. As a result, phytoplankton are mainly located near the water’s surface since they need to be closer to the area where the sun’s rays hit.
Another key difference between these two organisms is where they reside in the ocean. Because phytoplankton need to be closer to the sun to be able to conduct photosynthesis, they are located near the surface of the water. Zooplankton, on the other hand, reside just a little bit deeper in the upper surface of the water, where there is less sunlight available.
Everything You Need to Know About Zooplankton
Although zooplankton are essential players in the ecosystem of the ocean, they are often forgotten. To make sure that you don’t forget about these important organisms, here are a few quick facts about who they are, what do zooplanktons eat, and why they’re so important to the ecosystem.
- Like phytoplankton (ocean plants), zooplankton (animals) are a specific type of plankton.
- Zooplankton range in size, from microscopic to the size of a jellyfish.
- Zooplankton, like other types of plankton are too weak to swim on their own. Instead, they are known for drifting around the ocean, often being carried by the current and tide.
- Zooplankton play a key role in the food chain of the ocean. They are often consumed by larger marine life, such as fish and small sharks.
- Zooplankton feed on phytoplankton as their main food source. In some cases, they will also consume other zooplankton.
Do you have more questions about zooplankton and their ecological importance? If you would like to know more about them, feel free to leave your questions in the comments section!




Interesting blog post! I didn’t know zooplankton ate anything other than water.
Useful information. Thank you!
How to spawn zooplankton in ponds and what to do to make it live longer in pond.